+86 571 8659 2517
+86 180 5841 8258
info@zmuni.com
ZMUni provides comprehensive import and export clearance solutions with a strong focus on cosmetics and food, while also supporting other general product categories to ensure smooth, compliant, and efficient entry into the Chinese market.
China Import & Export Customs Clearance (Cosmetics, Food, and General Goods)
China Customs Import & Export Qualification Assistance
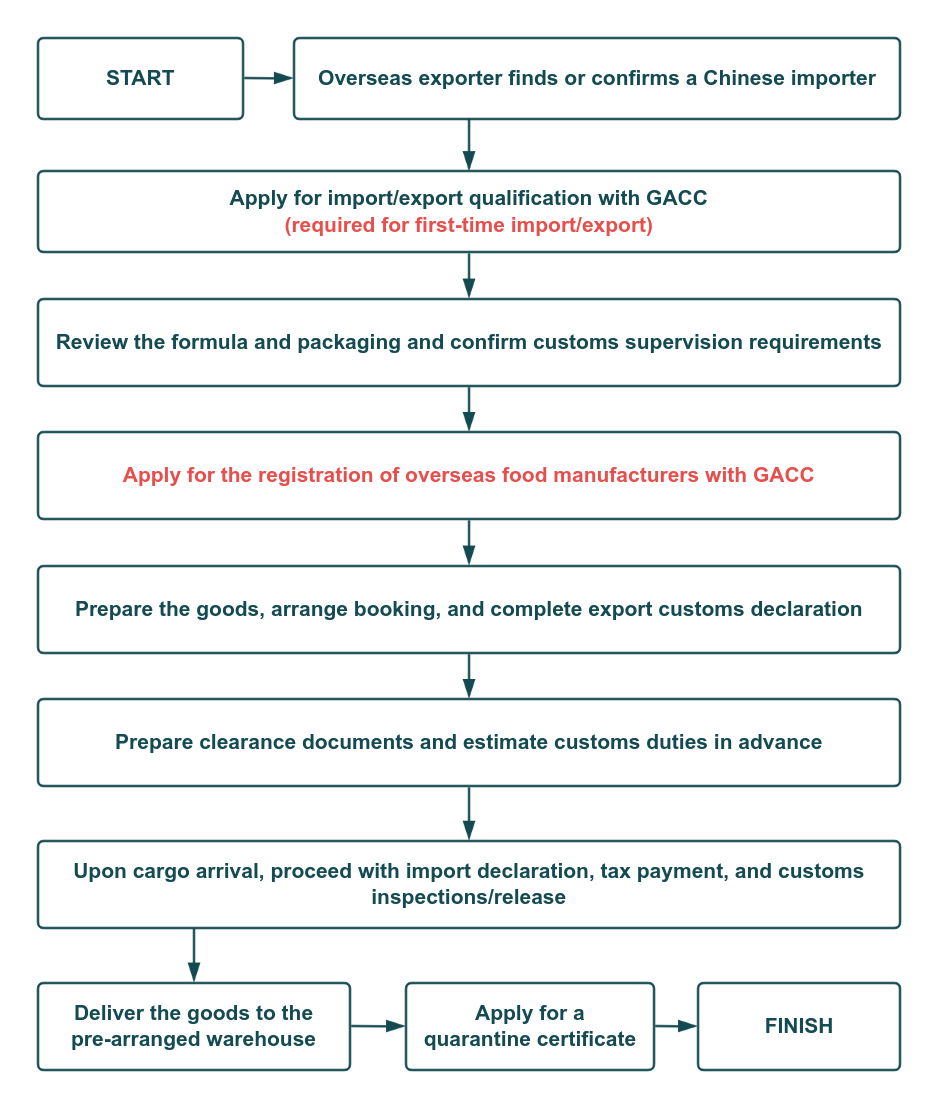
Importer Registration for Imported Food in China
GACC Overseas Manufacturers Registration of Imported Food
CITES Permits and Certificates

Business License | Cosmetics Registration/Notification Certificate |
10-Digit Customs Code | Original Label & Translation |
Contract | Chinese Label |
Invoice | Ingredient List |
Packing List | Hazard Identification Form of Risk Substance |
Bill of Landing | Trademark Registration Certificate |
Certificate of Origin | Goods List/Production Date Certificate |
Safety Commitment Letter | Customs Declaration Power of Attorney |
Safety Compliance Guarantee | Approval Authorization Letter |
Business License | Food Importer/Exporter Registration |
10-Digit Customs Code | Original Label & Translation |
Contract | Chinese Label |
Invoice | Ingredient List |
Packing List | Third-Party Test Report |
Bill of Landing | Trademark Registration Certificate |
Certificate of Origin | Goods List/Production Date Certificate |
Sanitary Certificate/Free Sale Certificate | Customs Declaration Power of Attorney |
GACC Registration Number |
China requires all overseas manufacturers of imported food to complete registration with the General Administration of Customs (GACC). This obligation—effective under Decree 248 since January 1, 2022—applies to food production, processing, and storage facilities exporting to China. Once approved, enterprises receive an In-China Registration Number, which must be printed on product packaging. Registration is valid for five years.
Certain 18 categories of higher-risk food (e.g., meat, dairy, aquatic products, nuts, grains, special dietary foods, health foods, etc.) must be recommended by the competent authority of the exporting country, while all other general pre-packaged foods can be self-registered directly by the manufacturer.
For a full explanation of the registration routes, required documentation, and ZMUni's support for GACC registration, please refer to our Pre-packaged Food Compliance Services.
Aquatic Wildlife Permits – Operation, utilization, and trade of aquatic wildlife in compliance with Chinese law.
Convention Certificates – Documentation for products regulated under international agreements, e.g., CITES Permits.
Assistance with permit applications, supporting documentation, and regulatory liaison.
Endangered species refer to wild animals and plants at high risk of extinction due to human activity or habitat loss. From a regulatory perspective, this includes species listed under the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES) and those protected under China's national wildlife protection lists.
Common examples of endangered species include:
Panax quinquefolius (American ginseng)
Aquilaria sinensis (Agarwood)
Cyathea medullaris (Black tree fern)
Prionace glauca (Blue shark)
Acipenser naccarii (Adriatic sturgeon)
Acipenser baerii (Siberian sturgeon)
For products that do involve endangered species, importers must follow China's regulatory procedures: applying to the appropriate agricultural or forestry authority, obtaining an approval document, and securing a CITES import permit before import. For more information, please refer to Import or Export Endangered Species: Apply for CITES Permits and Certificates in China.
Common Challenges | Implications |
Incomplete or incorrect documents (e.g., missing GACC registration numbers, invoices, packing lists, certificates of origin, CITES permits, or incorrect information) | Goods may be held at the port, fines imposed, customs clearance delayed, and demurrage fees incurred |
Incorrect product classification (wrong HS code leading to inaccurate duty calculation) | Additional duties and fines may apply; goods could be detained |
Unpaid duties and VAT (failure to pay customs duties or VAT on time) | Goods cannot be cleared; late payment penalties may accrue |
Intellectual property issues (goods suspected of infringing IP, such as counterfeit brands) | Goods may be seized; the company could face legal action and fines |
Non-compliant packaging or labeling (packaging or labels do not meet import/export requirements, e.g., missing required information or using incorrect language) | Goods may be returned or require repackaging, causing customs clearance delays |
Q: What additional documents are required for alcohol-containing perfumes?
A: Perfumes containing ethanol are considered hazardous chemicals. Companies must provide a Hazard Classification Report. Customs declaration must include the hazard class and UN number. Failure to declare may result in penalties under import/export regulations.
Q: Are there any special permits required for skincare products containing ginseng?
A: Check whether the ginseng is a CITES-listed endangered species.
If yes, an Import Permit is required.
If it is cultivated ginseng, provide a source declaration and test report to ensure proper HS code declaration and avoid clearance delays.
Q: Is registration or notification required for cosmetics imported in bulk and then repackaged in China?
A: Bulk cosmetics imported for repackaging are treated as cosmetic ingredients during import. After repackaging, the products should be registered or filed as domestically produced cosmetics. No registration or filing certificates are required at the import stage.
Q: Is an import permit required for cosmetics in China?
A: Before customs declaration, the domestic responsible party must obtain NMPA registration or notification for the imported cosmetics. The domestic consignee's registration must also be completed. Additionally, if the product contains endangered species, an import permit for endangered species is required.
Q: How long does it take to receive a response after submitting a GACC self-registration application?
A: The estimated response time is typically 5–10 working days. Actual timing may vary depending on factors such as product quantity, ingredient complexity, and information about production-related companies. Applicants can track the approval status directly through the system.
Q: Is a sanitary/health certificate mandatory for imported food customs clearance in China?
Yes. The sanitary certificate issued by the exporting country is generally authoritative and essential for public safety. Imported food cannot clear customs without this certificate. After customs clearance in China, the authorities will also conduct random sampling and testing of the imported food. An Imported Food Circulation Sanitary Certificate will be issued only after passing these inspections. This certificate is mandatory for the food to be legally marketed and sold in China.
Q: What is the difference between cross-border e-commerce imports and general trade imports?
A: Cross-border e-commerce imports do not require certain registrations or certificates, such as those needed for health foods, and are sold only through e-commerce platforms. Each person is limited to 26,000 RMB per year, and products are not for resale. In contrast, general trade imports require full registration or notification, allowing commercial sales. Key differences include tax rates, required qualifications, and documentation.
Q: What if the declared import price is considered too low by customs?
A: Provide supporting documents such as the original invoice, payment proof, and transaction records for the same batch. If there are related-party transactions affecting price, proactively explain to customs. Under reporting can be treated as smuggling; Shanghai authorities have previously investigated cases that led to criminal charges.
Last Updated on: December 11, 2025
+86 571 8659 2517
+86 180 5841 8258
info@zmuni.com